[Up]
[SIGAda]
[ACM]
ASIS Architecture
The following figure depicts the package architecture for the ASIS interface. A
tool or application using ASIS has visibility to the entire
declarative region of package Asis including all child packages. To
get a better understanding of how these packages are used, see
ASIS Notional Application Example,
Traverse Compilation Unit Example, and
Call Tree Example.
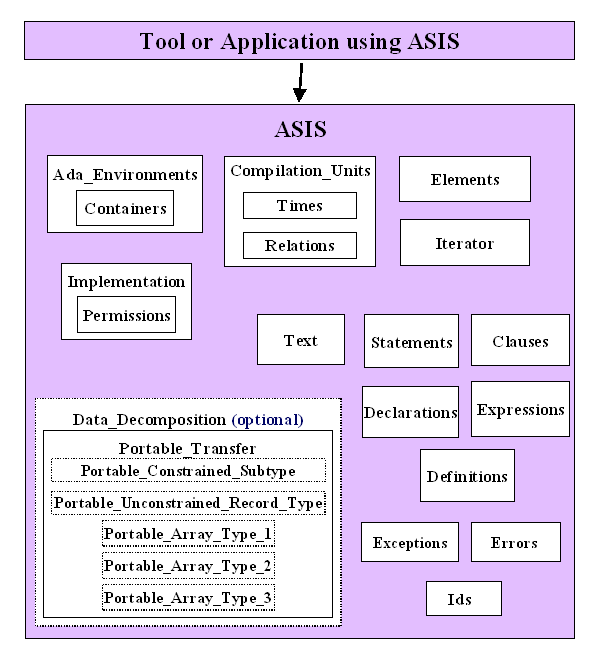
ASIS package architecture
package ASIS -
Package ASIS, together with its children, provides the interface
between an Ada environment (as defined by ISO/IEC 8652:1995) and any
tool requiring information fromit. Valuable semantic and syntactic
information is made available via queries through child packages of
package ASIS.Package Asis contains commontypes and subtypes used for
the ASIS interface and its child packages. Important common types
include:
- Type Context helps identify the compilation units considered
to be analyzable as part of the Ada compilation environment.
- Type Element is an abstraction of entities within a
logical Ada syntax tree.
- Element Kinds are a set of enumeration types providing a
mapping to the Ada syntax.
- Type Compilation_Unit is an abstraction for Ada compilation units.
- Unit Kinds are a set of enumeration types describing the various
kinds of compilation units.
- Type Traverse_Control provides a mechanism to control iterative
traversals of a logical syntax tree.
- Type Program_Text provides an abstraction for the program text
for a program's source code.
Package Asis also encapsulates implementor-specific declarations,
which are made available to ASIS and its client applications in an
implementor-independent manner. Package ASIS is the root of the ASIS
interface. All other packages are child packages of package
Asis. These packages are:
- Asis.Ada_Environments -
This child package encapsulates a set of
queriesthat map physical Ada compilation and program execution
environments to logical ASIS environments. An ASIS Context is
associated with some set ofAda compilation units maintained by an
underlying Ada implementation. After this association has been made,
this set of units is considered to bepart of the compile-time Ada
environment, which forms the outermost context of any compilation, as
specified in section 10.1.4 of the Ada Reference manual. This same
environment context provides the implicit outermost anonymous task
during program execution. If an Ada implementation supports the notion
of a program library or "library" as specified in section 10(2) of the
Ada Reference Manual, then an ASIS Context value can be mappedonto one
or more implementor libraries represented by Containers. More than one
context may be manipulated at a time. Important interfaces include:
Associate, Dissociate, Open, and Close. The type
Container and its supporting functions are provided in the child package
Asis.Ada_Environments.Containers.
-
Asis.Implementation -
This child package provides operations to
initialize and finalize the ASIS interface. It also provides queries
for the error status of the ASIS implementation. Its
child package
Asis.Implementation.Permissions
provides queries to determine options usedby an implementation.
-
Asis.Compilation_Units -
This child package encapsulates a set of
queries that implement the ASIS Compilation_Unit abstraction. It
defines queries that deal with Compilation_Units and the gateway
queries between Compilation_Units, Elements, and
Ada_Environments. More than one compilation unit may be manipulated at
one time. The child package
Asis.Compilation_Units.Times
encapsulates the time related functions
used within ASIS. A second child package,
Asis.Compilation_Units.Relations
encapsulates the semantic
relationship concepts used in ASIS. Relation queries provide
references to compilation units that are related,in some specific
fashion, to one or more given compilation units.
-
Asis.Iterator -
This child package encapsulates the Traverse_Element
mechanism to perform an iterative traversal of a logical syntax
tree. Duringthe traversal, ASIS can analyze the various elements
present and provideapplication processing via generic procedures
instantiated by the application using queries to decompose ASIS
elements into the logical semantic tree of the Ada program.
This key mechanism is the heart of most ASIS tools.
-
Asis.Elements -
This child package encapsulates a set of queries that
operate on all elements and some queries specific to A_Pragma
elements. Element_Kinds, defined in package Asis are defined as
enumeration types describing the various kinds of elements. ASIS
offers a hierarchical classification of elements. At the highest
level, the Element_Kinds type providesliterals that define "kinds" or
classes into which all non-nil elements are grouped. Element_Kinds
are: Not_An_Element, A_Pragma, A_Defining_Name, A_Declaration,
A_Definition, An_Expression, An_Association, A_Statement, A_Path,
A_Clause, and An_Exception_Handler. Elements in each of the
Element_Kinds classes, with the exception of An_Exception_Handler, can
be further classified by a subordinate kind at the next level in the
hierarchy.
-
Asis.Clauses -
This child package encapsulates a set of queries that
operate on the A_Clause element.
-
Asis.Declarations -
This child package encapsulates a set of queries
that operate on A_Defining_Name and A_Declaration elements.
-
Asis.Definitions -
This child package encapsulates a set of queries
thatoperate on A_Definition elements.
-
Asis.Expressions -
This child package encapsulates a set of queries
thatoperate on An_Expression and An_Association elements.
-
Asis.Statements -
This child package encapsulates a set of queries
that operate on A_Statement, A_Path, and An_Exception_Handler elements.
-
Asis.Text -
This child package encapsulates a set of operations to
access the text of ASIS Elements. This text is represented as logical
lines from the source code of the external representation of a
compilation unit. Type Line is defined to support program text
operations. It assumes no knowledge of the existence,
location, or form of the program text.
-
Asis.Errors -
This child package provides an enumeration type
identifying the error kinds used for the ASIS interface.
-
Asis.Exceptions -
This child package identifies all defined ASIS exceptions.
-
Asis.Ids -
This child package encapsulates a set of operations and
queries that implement the ASIS Id abstraction. An Id is a way to
identify a particular element (i.e., a unique reference to an Element)
which is efficient and persistent as long as the environment is not
recompiled.
-
Asis.Data_Decomposition -
This optional child package encapsulates a
setof operations to decompose data values using the ASIS type
information and a portable data stream, representing a data value of
that type. Its child package
Asis.Data_Decomposition.Portable_Transfer
provides support for logging
and delogging of application data using ASIS. Internal packages of
Asis.Data_Decomposition.Portable_Transfer include:
Portable_Constrained_Subtype, Portable_Unconstrained_Record_Type,
Portable_Array_Type_1 (for one dimensional arrays),
Portable_Array_Type_2 (for two dimensional arrays), and
Portable_Array_Type_3 (for three dimensional arrays).
[Up]
[SIGAda]
[ACM]
Last update 17 August 1998.
Questions, comments to
Clyde Roby (CRoby@IDA.Org)

